Sign into OpenAthens with local authentication systems
Introduction
It is possible to devolve the username and password part of OpenAthens to a local authentication system. From the users' perspective they will not need to remember additional OpenAthens credentials, instead using existing ones such as their network login. From an administrator's perspective you would not need to create or manage additional accounts as this is already being handled within your organisation.
Examples of local authentication systems include:
- Microsoft ActiveDirectory, ADFS or Azure
- IBM Tivoli
- LDAP
- NetIQ Access Manager
- Novell Access Manager
- OpenID Connect
- Ping Federate
- More
How do my local authentication system and OpenAthens work together?
OpenAthens still takes care of things like the access to resources, federations, permission set management and statistics - these remain under the control of the library - but the usernames and passwords are handed off to your local system where your IT team is already managing user accounts.
Permission set considerations
You should think about your existing subscriptions and decide whether all users should inherit your default permission set, or if you need to allocate specific permission sets to different groups of users. If you need to allocate specific permission sets you will need to release an additional attribute containing that permission set name. Permission set names appear in the following format:
<organisation prefix>#<name> e.g. edu#staff
User journey when local authentication system is integrated with OpenAthens
The diagram below shows the basic user journey to a resource both with and without a local authentication system being integrated:
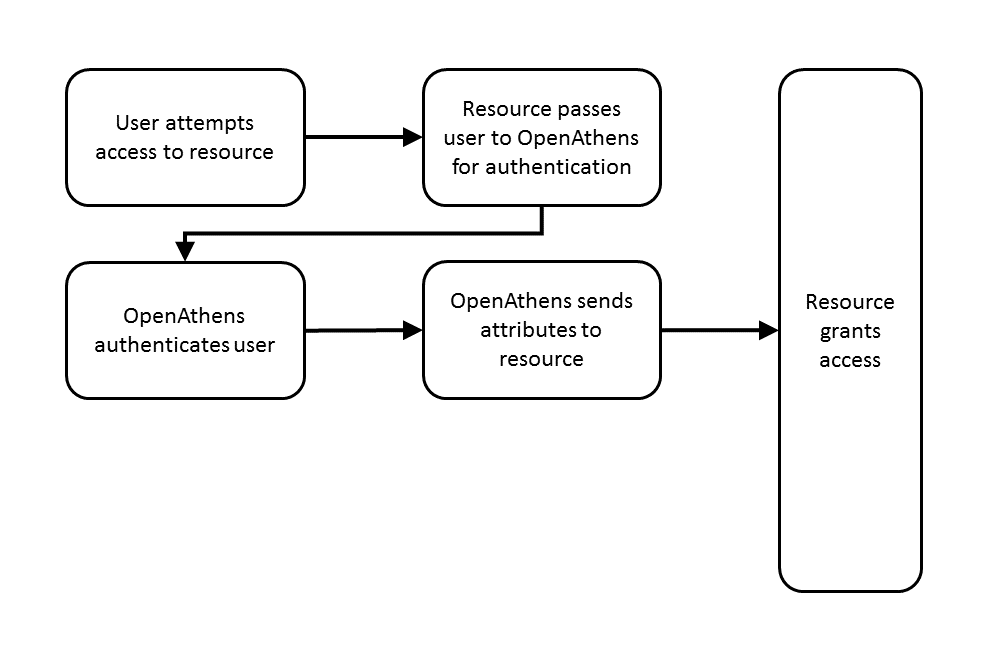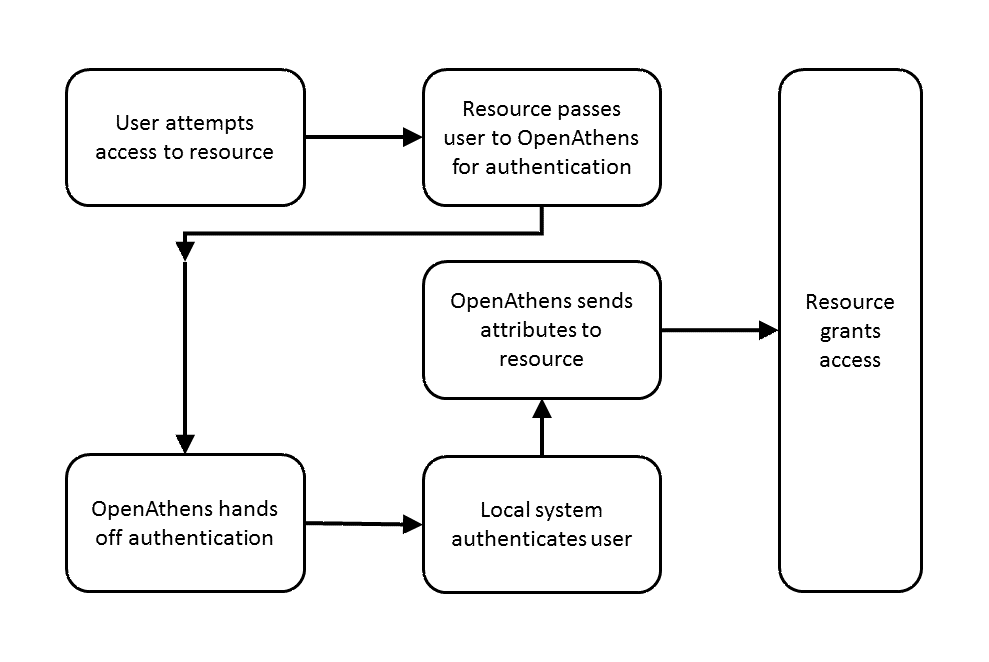
Help
We understand setting up new connections can be time-consuming, and administrators can run into difficulty setting these up themselves. As well as our service desk, we have consultancy services available to support customers setting up a new connection and your account manager will be happy to discuss options and prices with you.
Specific systems
